Forecast Accuracy and Reliability
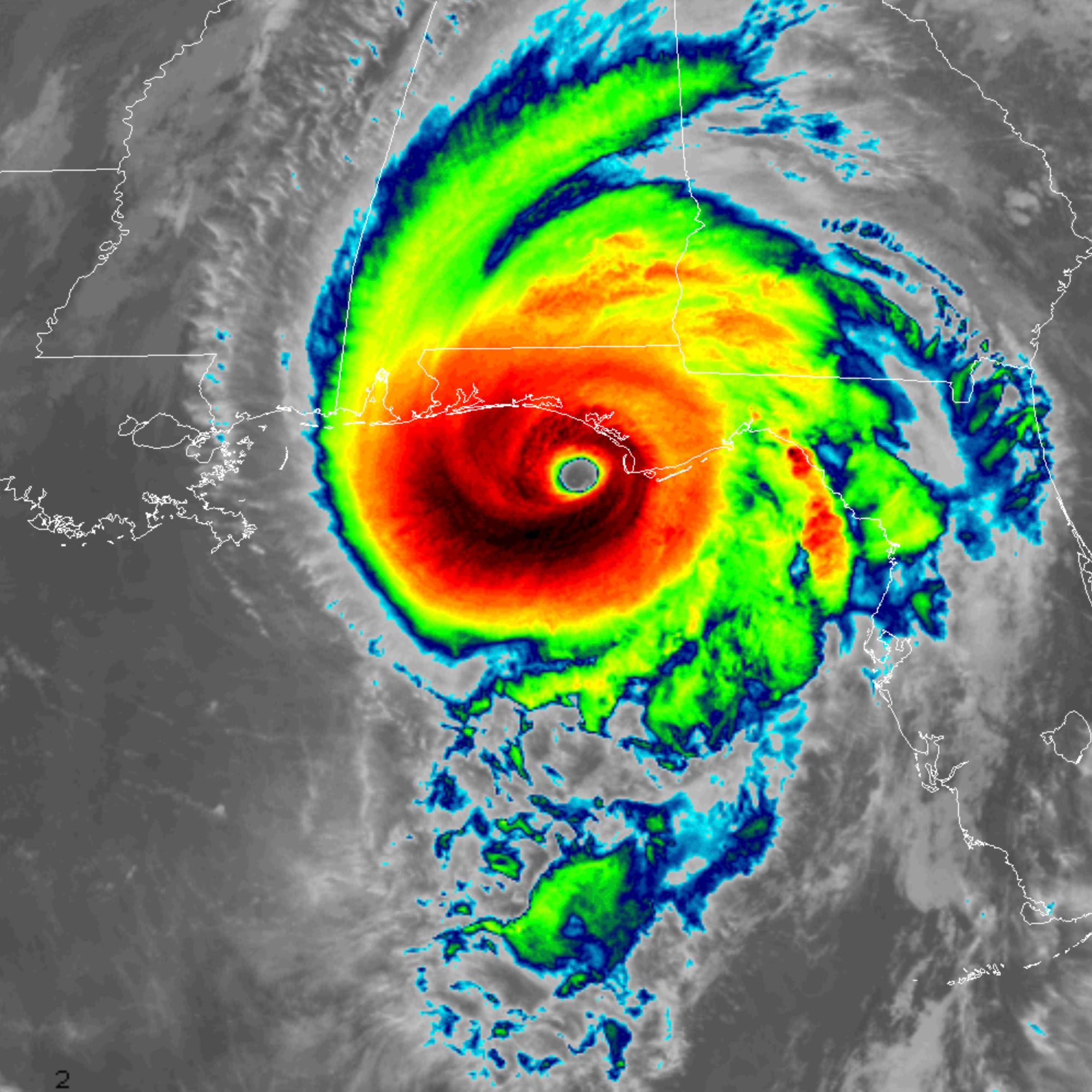
The accuracy of hurricane forecasts depends on various factors, including the availability and quality of data, the sophistication of forecasting models, and the skill of forecasters. While significant progress has been made in hurricane forecasting in recent decades, there are still limitations and uncertainties associated with the process.
Tracking hurricanes is crucial for timely preparation and response. The latest forecast indicates that Hurricane Beryl is expected to make landfall on the eastern coast. For the most up-to-date information on its path and potential impact, visit the beryl track page.
Stay informed and take necessary precautions to ensure safety.
Data Availability and Quality
The accuracy of hurricane forecasts relies heavily on the availability and quality of data. This includes observations from weather stations, satellites, radar, and aircraft reconnaissance. The more comprehensive and accurate the data, the better the forecasts will be.
Forecasting Models, Hurricane forecast
Hurricane forecasting models are computer programs that use mathematical equations to simulate the behavior of hurricanes. These models are constantly being improved, but they are still limited by the complexity of the atmosphere and the ocean. As a result, forecasts can sometimes be inaccurate, especially for long-range predictions.
Hurricane forecasts provide crucial information for preparing for these powerful storms. For instance, the hurricane beryl forecast offers insights into the potential path and intensity of this specific storm. By staying informed about hurricane forecasts, individuals and communities can take proactive steps to mitigate risks and ensure safety during hurricane season.
Forecaster Skill
The skill of the forecaster also plays a role in the accuracy of hurricane forecasts. Forecasters must have a deep understanding of hurricane dynamics and be able to interpret complex data. They must also be able to make sound judgments about the future path and intensity of hurricanes.
Limitations and Uncertainties
Despite the progress that has been made in hurricane forecasting, there are still limitations and uncertainties associated with the process. These include:
- The chaotic nature of the atmosphere: The atmosphere is a complex and chaotic system, which makes it difficult to predict the exact path and intensity of hurricanes.
- The lack of data: There are still large areas of the ocean that are not well-observed, which can make it difficult to track and forecast hurricanes.
- The limitations of forecasting models: Forecasting models are still limited by the complexity of the atmosphere and the ocean, which can lead to inaccurate forecasts.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Forecasts
There have been many successful hurricane forecasts in recent years. For example, the National Hurricane Center accurately predicted the path and intensity of Hurricane Katrina in 2005, which allowed millions of people to evacuate before the storm made landfall. However, there have also been some unsuccessful hurricane forecasts. For example, the National Hurricane Center failed to predict the intensity of Hurricane Andrew in 1992, which resulted in widespread damage and loss of life.
Data Collection and Analysis

Accurate hurricane forecasting relies heavily on comprehensive data collection and meticulous analysis. Meteorologists employ various methods to gather data from multiple sources, including:
- Weather stations: Ground-based weather stations measure atmospheric conditions, such as temperature, pressure, humidity, and wind speed and direction.
- Buoys: Buoys deployed in oceans and coastal waters collect data on wave height, water temperature, and currents.
- Aircraft: Reconnaissance aircraft fly into hurricanes to gather detailed measurements of wind speed, pressure, and temperature.
- Satellites: Satellites monitor hurricanes from space, providing images of cloud patterns, precipitation, and wind fields.
Once collected, this vast amount of data is analyzed using sophisticated computer models. These models simulate hurricane behavior based on physical equations that describe atmospheric processes. By incorporating real-time data, meteorologists can predict hurricane paths and intensities with increasing accuracy.
Weather Models and Supercomputers
Weather models are mathematical representations of the atmosphere. They use complex algorithms to simulate the interactions between different atmospheric components, such as temperature, pressure, and wind. Supercomputers are powerful computers that can perform these complex calculations rapidly, enabling meteorologists to run multiple model simulations and produce more accurate forecasts.
By combining real-time data with advanced weather models and supercomputers, hurricane forecasters can provide timely and reliable predictions, helping communities prepare for and mitigate the impacts of these powerful storms.
Impact and Mitigation: Hurricane Forecast

Hurricanes can have devastating impacts on coastal communities, including wind damage, flooding, and storm surge. Wind damage can cause widespread destruction of buildings, infrastructure, and vegetation. Flooding can inundate homes and businesses, causing significant damage and displacement. Storm surge, a wall of water pushed ashore by the hurricane’s winds, can cause catastrophic flooding and erosion.
There are a number of strategies that can be used to mitigate hurricane risks, including evacuation plans and coastal protection measures. Evacuation plans help to ensure that residents have a safe place to go in the event of a hurricane. Coastal protection measures, such as seawalls and levees, can help to protect communities from flooding and storm surge.
Hurricane Forecasts and Risk Mitigation
Hurricane forecasts play a vital role in saving lives and property. By providing timely and accurate information about the track and intensity of hurricanes, forecasts help communities to prepare for and respond to these storms. In the United States, the National Hurricane Center (NHC) issues hurricane forecasts that are used by emergency managers, government officials, and the public to make decisions about evacuation and other protective measures.
- In 2005, Hurricane Katrina devastated the Gulf Coast of the United States. The NHC’s forecasts helped to save lives by providing timely warnings about the storm’s track and intensity. The forecasts allowed residents to evacuate to safety before the storm made landfall.
- In 2017, Hurricane Harvey made landfall in Texas as a Category 4 hurricane. The NHC’s forecasts helped to save lives by providing timely warnings about the storm’s track and intensity. The forecasts allowed residents to evacuate to safety before the storm made landfall.